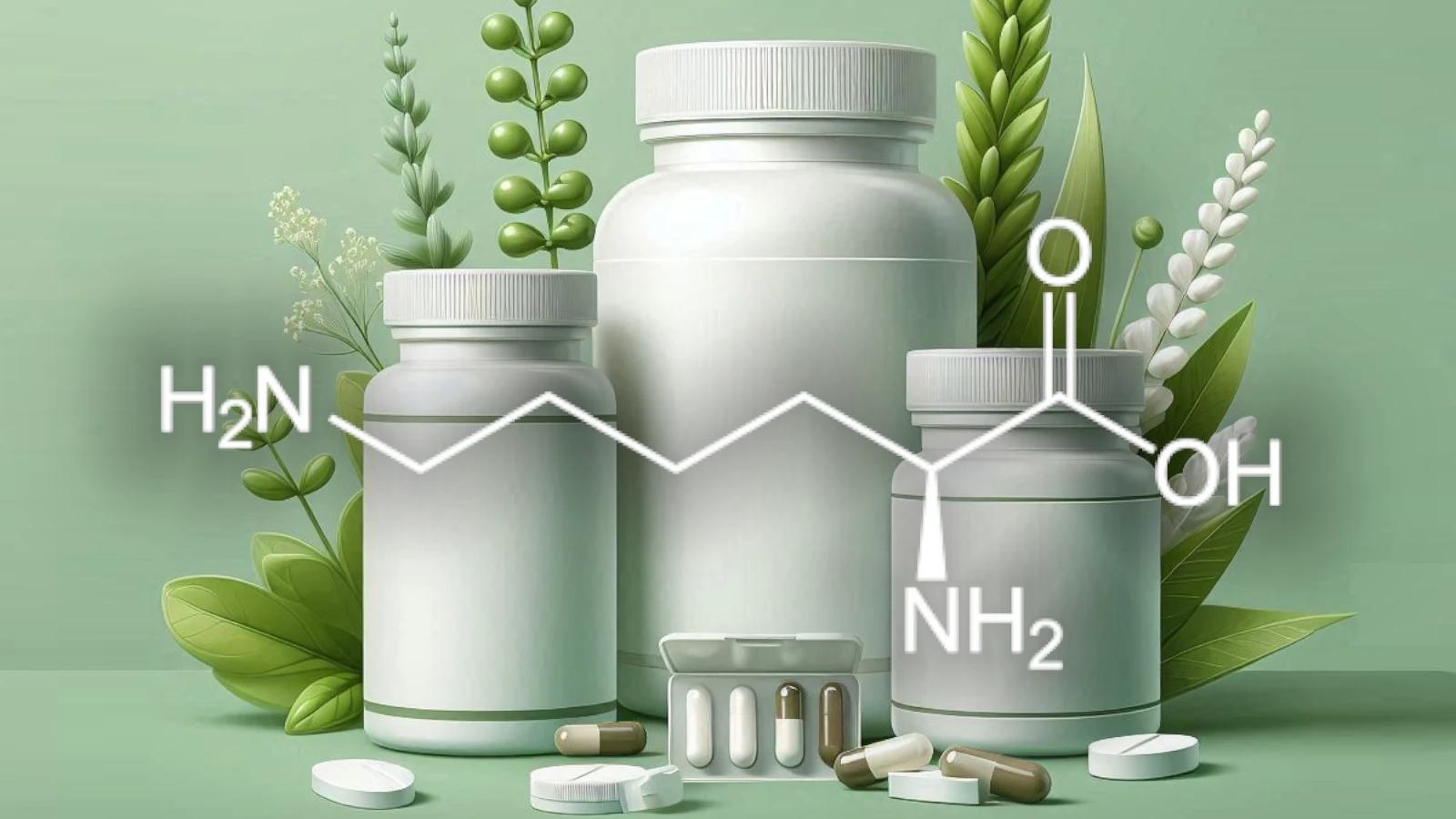
Lysine and L-lysine are essential amino acids that play crucial roles in human health and nutrition.
While they are often used interchangeably, there are significant differences between the two forms.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for optimizing health benefits, particularly in managing conditions like cold sores caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
This article delves into the differences between lysine and L-lysine, exploring their biological activity, dietary sources, and potential applications in supporting overall health and preventing herpes outbreaks.
What is Lysine?
Lysine, scientifically known as α-lysine, is one of the essential amino acids that the human body cannot synthesize on its own.
It must be obtained through dietary sources or supplements.
Lysine is vital for numerous physiological processes, including protein synthesis, hormone production, and calcium absorption.
It also plays a crucial role in the formation of collagen, a protein that provides structure and support to various tissues in the body, such as skin, tendons, and bones.
Maintaining adequate levels of lysine is essential for overall health and well-being.
What is L-Lysine?
L-lysine is the biologically active form of lysine that the body can effectively utilize for various functions.
The "L" stands for "levo," indicating the specific spatial arrangement of the amino acid's atoms, which allows it to participate in biochemical reactions.
In most nutritional and health contexts, L-lysine is the relevant form, as it is the one that the body can use for protein synthesis, collagen formation, and other vital processes.
Understanding the distinction between lysine and L-lysine is crucial when discussing supplementation and health benefits, as L-lysine is the form that provides the most effective support for the body.
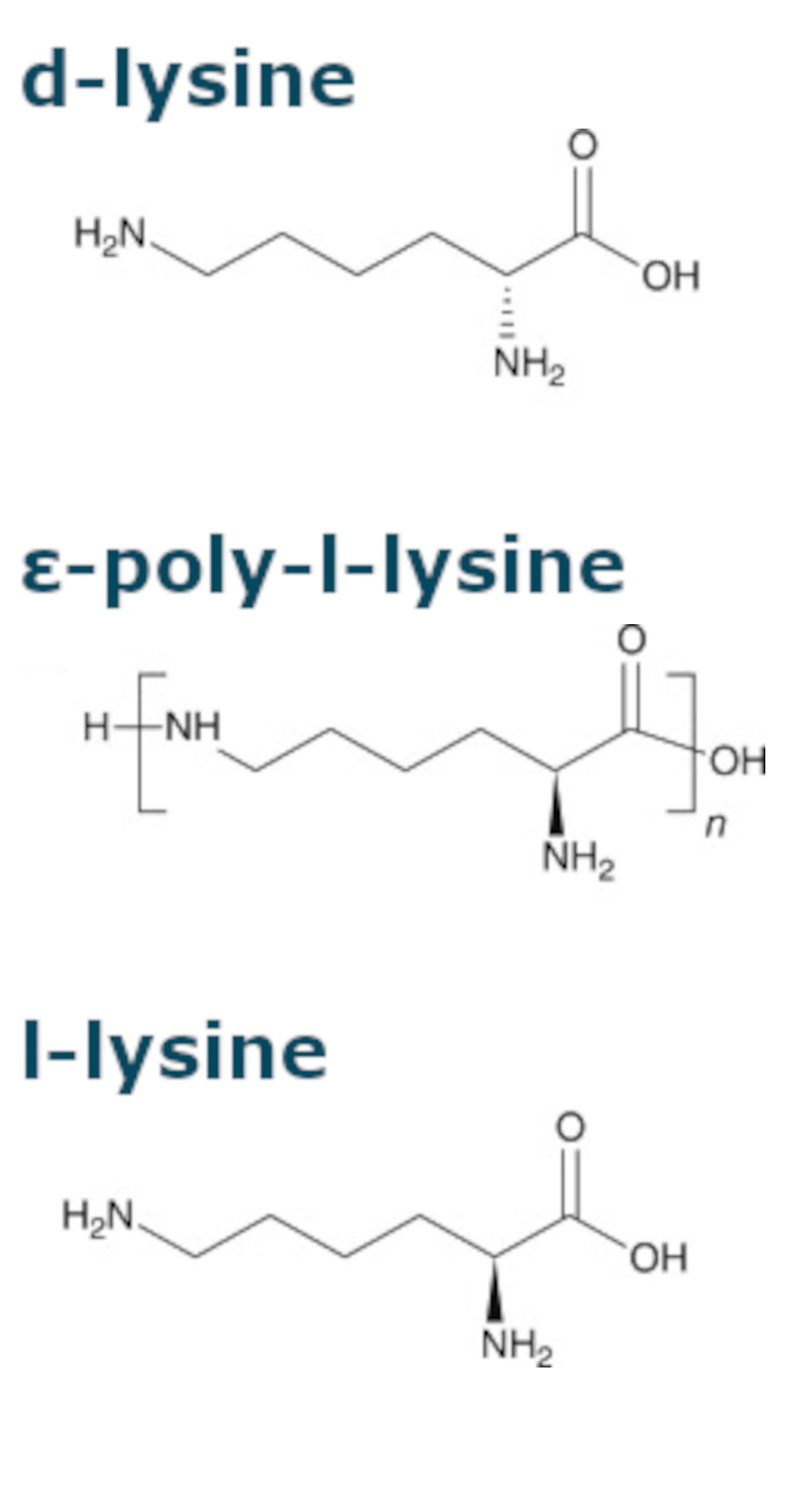
Key Differences Between Lysine and L-Lysine
- Biological Activity: L-lysine is the active form that the body utilizes for protein synthesis, collagen formation, and other essential functions. In contrast, the term "lysine" can encompass both active and inactive forms, leading to potential confusion and misunderstandings. It is important to specify L-lysine when discussing its benefits and applications.
- Usage in Supplements: Most dietary supplements contain L-lysine, as it is the form that provides the most effective health benefits. When discussing supplementation, it is crucial to specify L-lysine to ensure clarity regarding its efficacy and to differentiate it from other forms that may not provide the same level of support.
- Chemical Structure: The structural differences between L-lysine and D-lysine affect their biological roles and interactions within the body. L-lysine is involved in numerous metabolic pathways and can participate in various biochemical reactions, while D-lysine does not contribute effectively to protein synthesis and other vital processes.
| Characteristic | Lysine | L-Lysine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Biological Activity | Can refer to both active and inactive forms | The biologically active form utilized by the body |
| Usage in Supplements | May refer to different forms, including inactive ones | The preferred form in dietary supplements | |
| Chemical Structure | Includes both L-lysine and D-lysine | The specific spatial arrangement that allows participation in biochemical reactions | |
The Role of Lysine in the Body
Lysine, particularly in its L-lysine form, is involved in several critical biological processes that are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
These processes include:
- Protein Synthesis: As a building block of proteins, L-lysine is necessary for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues throughout the body.
It contributes to the production of structural proteins, enzymes, and other important molecules.
- Calcium Absorption: L-lysine enhances the body's ability to absorb and utilize calcium, which is vital for maintaining strong bones and teeth.
Adequate calcium absorption is essential for preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
- Collagen Formation: L-lysine is a key component in the production of collagen, a protein that provides structure, elasticity, and support to various tissues, including skin, tendons, ligaments, and bones.
Collagen is essential for maintaining healthy skin and joint function.
- Hormone Production: L-lysine plays a role in the synthesis of hormones and enzymes that regulate various bodily functions, such as metabolism, growth, and development.
It contributes to the production of hormones like insulin and growth hormone.
Dietary Sources of Lysine
To maintain adequate levels of lysine, particularly in its L-lysine form, it is essential to consume a balanced diet rich in foods that are naturally high in this essential amino acid.
Some of the best dietary sources of lysine include:
- Meat: Red meat, pork, and poultry are among the richest sources of lysine, providing high concentrations of this amino acid in a readily available form.
- Dairy Products: Cheese, particularly parmesan, and other dairy products like milk and yogurt provide significant amounts of lysine.
Dairy is an excellent source of L-lysine for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Fish: Certain fish, such as cod, sardines, and tuna, are also excellent sources of lysine, making them a great addition to a balanced diet.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and soy products, such as tofu and tempeh, are excellent plant-based sources of lysine for vegetarians and vegans.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help ensure adequate intake of this essential amino acid.
- Eggs: Eggs are another good source of lysine, providing a complete and bioavailable form of this amino acid.
They are a versatile and convenient addition to a healthy diet.
Lysine vs L-Lysine for Cold Sores
Cold sores, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), are a common viral infection characterized by painful blisters around the lips and mouth.
Many individuals seek ways to manage or prevent these outbreaks, leading to interest in the potential role of L-lysine.
Research suggests that L-lysine may help prevent HSV outbreaks by inhibiting the activity of arginine, another amino acid that promotes HSV replication.
By blocking arginine's effects, L-lysine may reduce the frequency and severity of cold sore outbreaks.
While the effectiveness of L-lysine in treating active cold sore outbreaks is less clear, some studies have shown that regular supplementation with L-lysine may help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
A common recommendation for those considering L-lysine for cold sore prevention is a daily dose of 1,000 to 3,000 mg.
However, individual needs may vary, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.

Potential Side Effects and Considerations
L-lysine is generally considered safe when taken in appropriate doses.
However, some individuals may experience mild side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort or diarrhea.
It is essential to be cautious with high doses, especially for individuals with certain health conditions, such as kidney disease, as excessive intake may lead to potential complications.
Additionally, those taking medications should consult with a healthcare professional before starting any L-lysine supplementation to ensure compatibility and avoid any adverse interactions.
Conclusion
In summary, lysine and L-lysine refer to the same essential amino acid, with L-lysine being the biologically active form that the body utilizes for various physiological functions.
Lysine is crucial for protein synthesis, calcium absorption, collagen formation, and hormone production, all of which are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
When it comes to managing cold sores caused by the herpes simplex virus, L-lysine may offer preventive benefits by inhibiting the replication of the virus and reducing the frequency of outbreaks.
However, its effectiveness in treating active outbreaks remains inconclusive.
For individuals seeking to enhance their lysine intake, a balanced diet rich in protein sources, such as meat, dairy, fish, legumes, and eggs, can provide a natural and bioavailable source of this essential amino acid.
Supplementation with L-lysine may also be beneficial, particularly for those prone to cold sore outbreaks.
As with any health-related decision, consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable to determine the best approach for individual needs and circumstances, taking into account factors such as overall health, dietary preferences, and any underlying conditions or medications.
Bravado Labs Advanced Lysine Immune Boost
Why we love it:
- Verified Customer Favorite
- High Quality Ingredients
As an affiliate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Recommended Supplements for Herpes Management
Simplix Viral Defense
Cold Sore & HSV Support
Simplix Viral Defense
Cold Sore & HSV Support
Synergistic formula combining L-Lysine, shiitake mushroom, and marine bioactives for comprehensive immune support.
SHOP NOW & SAVE 15%